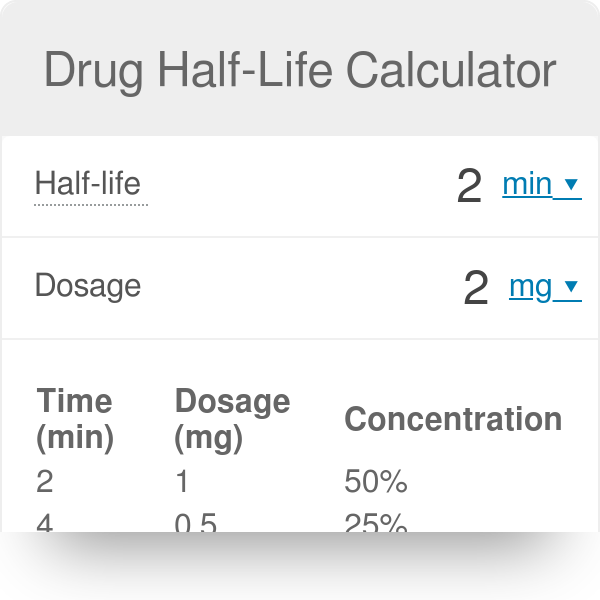
half life formula pharmacology
Authors H Boxenbaum 1 M Battle. An alternative half-life equation exists that relates half-life to other pharmacokinetic parameters known as the volume of distribution and clearance Equation 3.
This final equation shows the relationship between t 12 and the elimination rate constant.
. N t N 0 0. Ln Ao A k t. Half life formula half life equation Half life 0693k.
In this lesson we will define what a half-life is in pharmacological terms and explain how it is relevant. In pharmacology the concepts of half-lives and steady states are relevant to a patient. T 1 2 ln 2 V D C L displaystyle t_frac 12frac ln 2cdot V_DCL.
5 t T Nt N_0 times 05tT N t N 0 0. 1000000 micrograms mcg are in 1 g. Half life formula By using the following decay formula the number of unstable nuclei in a radioactive element left after t can be calculated.
Half-life is determined by clearance CL and volume of distribution V D and the relationship is described by the following equation. If 800mg is administered at 100 am how much of the drug would be eliminated after 24 hours. 1000000000 nanograms ng are in 1 g.
The elimination half-life of a drug is a pharmacokinetic parameter that is defined as the time it takes for the concentration of the drug in the plasma or. Click to see full answer In this regard how do you calculate half life in pharmacology. Pharmacologically this is expressed as the Peak minus Through concentrations divided.
Affiliation 1 Wyeth. Where t 12 is the half-life of the particle t is the elapsed time N 0 is the quantity in the beginning and N t is the quantity at time t. Drug X has a half-life of 8 hours.
Relative Bioavailability Absolute Bioavailability Volume of Distribution. This is the number of times the drugs dosage would be cut in half. What is half life in pharmacokinetics.
The definition of half-life t 12 is the time required for the concentration to fall to 50 of its current value. Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology. Apparent half-life t 12.
View PHARMACOLOGY FORMULASpdf from FOP PHAR at University of Santo Tomas. If 600mg is administered at 800 pm how much of the drug would be eliminated after 24 hours. It then takes 05 50 as a decimal and increments it to the power of.
K first order rate constant. This rate is constant in first-order kinetics and is independent of drug concentration in the body. The most important conversions that you should be aware of in a practical sense in medicine are the.
Pharmacology Drug Half Life Practice Questions. To do this we are looking for a time t 12 in which. This was derived by assuming a 1-compartment model and linear elimination.
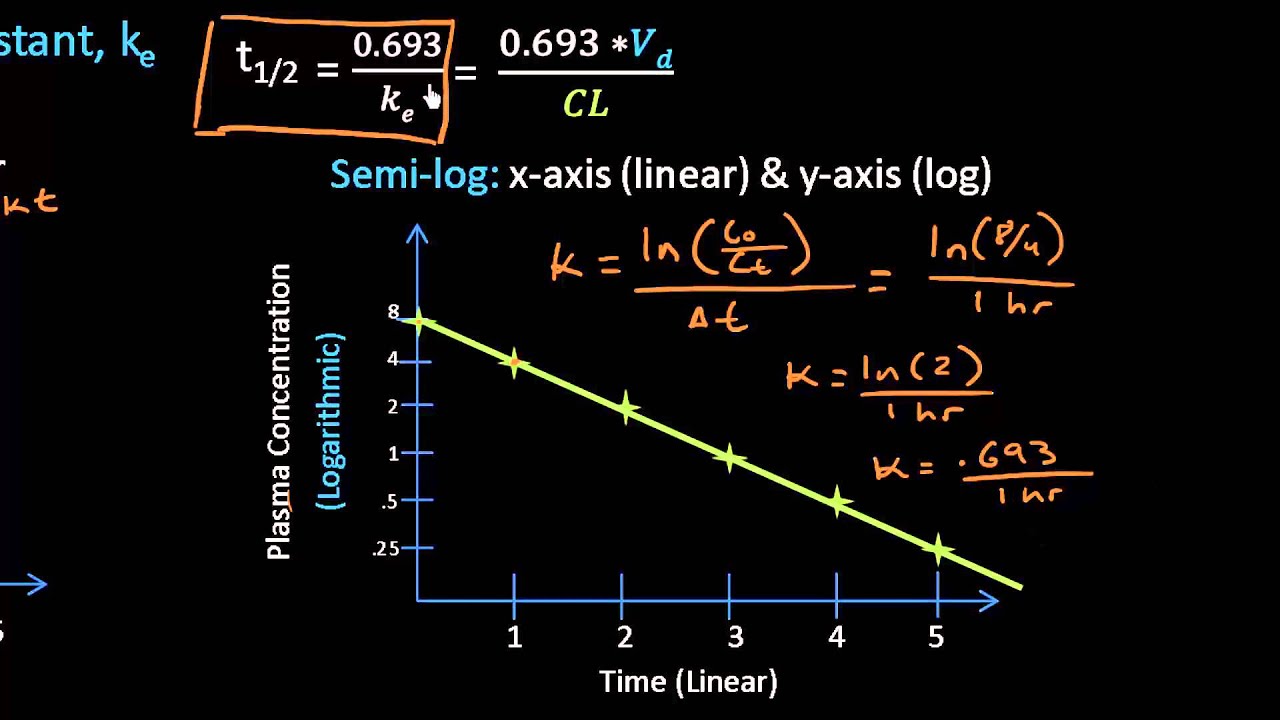
3 4 Equation 1. Fractional rate of drug removal from the body. λ is the slope of the plasma concentration-time line on a logarithmic y scale.
Elimination half life t12 Is the time taken for plasma concentration of a drug to reduce by 50 of its initial value After 4 half lives elimination is 94 complete kel the log of 2 divided by the t12 0693t12 Likewise Cl kel x Vd so Cl 0693 Vdt12 t12 0693 x Vd Cl Kel elimination constant. You can find the half-life of a radioactive element using the formula. 2 A 0 in order to calculate the half-life of the reactant A and isolate the time of the half-life t12.
In the simplest caseand the most useful in designing drug dosage regimensthe body may be considered as a single compartment as illustrated in Figure 32B of a size equal to the volume of distribution V. Elimination rate constant λ. The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL Volume of distribution Vd and clearance CL are required to calculate this variable.
Drug A has a half-life of 4 hours. Formula Half Life 0693 KE Half Life 0693 0015 462 hours So this means that the drug will take 462 hours to remove roughly half. 5 t T.
The half time or life of a dose is defined as the period of time after administration in either hours of minutes in which the dosage reaches half of its concentration in the plasma. Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology. The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL Volume of distribution Vd and clearance CL are required to calculate this variable.
Half-life t 12 is the time required to change the amount of drug in the body by one-half during elimination or during a constant infusion. In some cases such as for controlled-release preparations the rate of decline of the drug plasma. Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology J Clin Pharmacol.
See the video below for more details. This equation is used in the calculator when solving for half-life time. T 1 2 1 A 0 k displaystyle t_ 12 frac 1 ce A_ 0k As you can see the half-life of the second order reactions depends on the initial concentration and rate constant.
The function calculates the number of half-lifes experienced by the drug by taking the number of days 24 hours in a day and dividing that by the total number of hours it takes for a half-life of that drug. A pharmacological definition and an analysis to its formula. Half-life t½ is the time required to reduce the concentration of a drug by half.

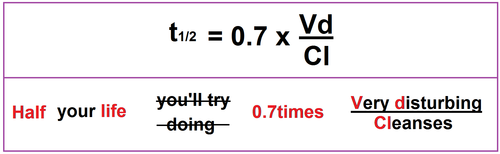
My Notes For Usmle Pharmacokinetics Formulas Mnemonic
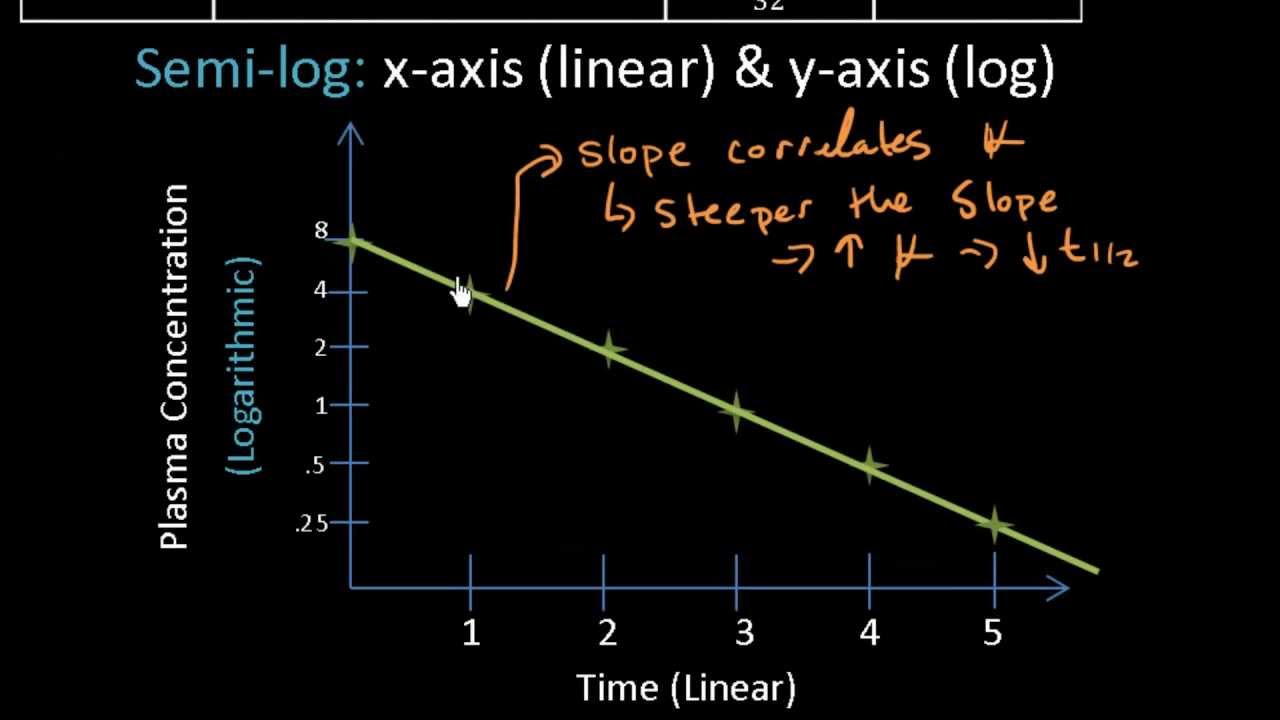
Drug Half Life An Overview Pharm Lect 10 Youtube
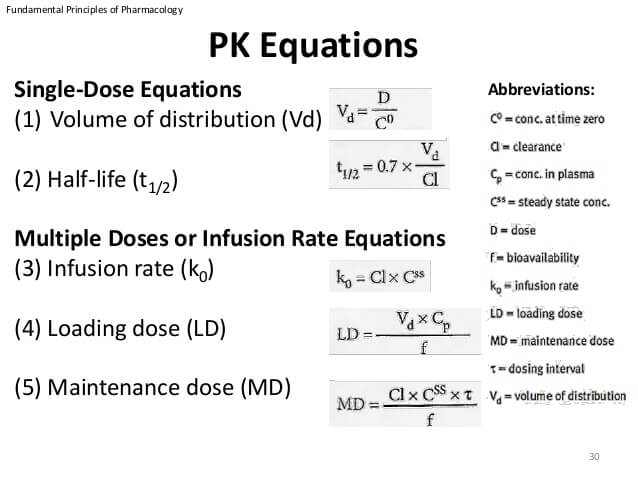
Pharmacokinetics Mnemonics Epomedicine
First Order Elimination Rate Constant And Half Life A Closer Look Lect 11 Youtube